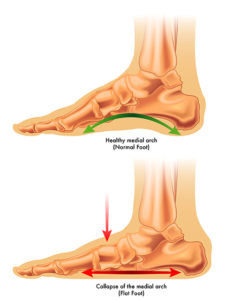
Damage to the posterior tibial tendon is the most common cause of adult acquired flatfoot deformity (AAFD)
The posterior tibial tendon is one of the most important tendons of the leg. It starts at a muscle in the calf, travels down the inside of the lower leg and attaches to the bones on the inside of the foot.
The main function of this tendon is to hold up the arch and support your foot when you walk. If the tendon becomes inflamed or torn, the arch will slowly collapse.
Women and people over 40 are more likely to develop problems with the posterior tibial tendon. Other risk factors include obesity, diabetes, and hypertension. Having flat feet since childhood increases the risk of developing a tear in the posterior tibial tendon. In addition, people who are involved in high impact sports, such as basketball, tennis, or soccer, may have tears of the tendon from repetitive use.